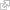Childbirth
Childbirth is all of the phenomena occurring in the body of the pregnant woman that lead to the birth of her child. It generally occurs between the 37th and the 42nd week of pregnancy. Childbirth taking place before the 37th week is considered premature. If it occurs more than 10 days after the projected delivery date, it is referred to as a prolonged pregnancy. Childbirth normally occurs via natural means, but surgical intervention, the cesarean section, is sometimes necessary.
The progression of childbirth
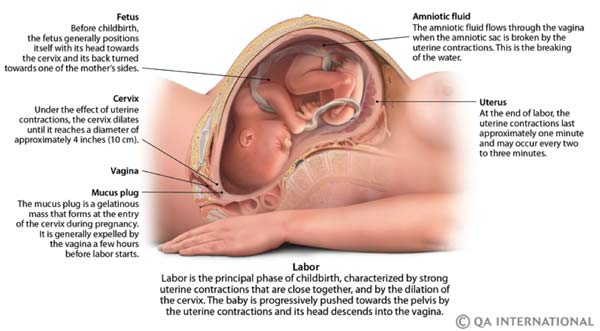
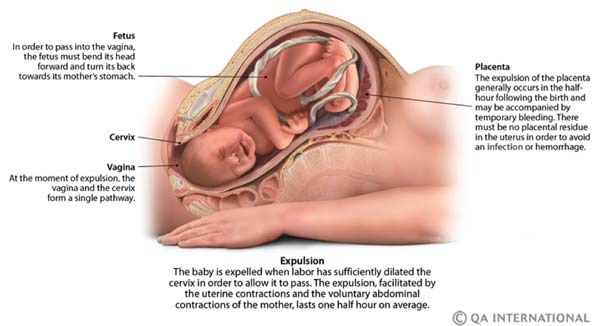
During the last weeks of pregnancy, the fetus generally positions its head in the direction of the cervix. Childbirth begins when a hormone, oxytocin, triggers the dilatation of the cervix and the spasmodic contractions of the uterine muscles. The amniotic sac may break, releasing the amniotic fluid, while the uterine contractions become more frequent and intensify. This is labor. The expulsion of the child occurs on average after 10 hours of labor, but this duration is often shorter in women who have already given birth. Childbirth ends with the expulsion of the placenta.
Childbirth in a medical environment
In industrialized countries, the majority of births take place in a medical environment in the event intervention is needed in case of complication. A nurse or a midwife follows the progress of the labor by regularly evaluating the dilatation of the cervix and monitoring the uterine contractions. The fetal heartbeat is also monitored using an ultrasound sensor placed on the mother’s abdomen (fetal monitoring). The midwife is authorized to deliver the baby, but a doctor intervenes in case of complication or if the birth presents certain risks, specifically in the case of premature birth or multiple pregnancy. The pain felt by the mother may be alleviated by epidural anesthesia. Epidural anesthesia is given during childbirth in order to locally suppress the painful sensations of contractions without altering mother’s consciousness. The anesthetic drug is injected into the lower back, generally between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae, in the epidural space surrounding the spinal cord. It does not present any risk for the fetus.
Today neither fat nor fragrant plants are needed to create perfume. Advances in chemistry have made it possible for perfumers to artificially recreate almost every scent… or invent entirely new ones!
Childbirth at home
Throughout the world, the majority of births take place at home. In industrialized countries, a woman may plan to give birth at home if her pregnancy does not demonstrate any risk: single fetus presenting normally, placenta in proper position, etc. However, this type of childbirth requires that certain precautions be taken. The practitioner who accompanies the labor must have the medical equipment available to handle possible complications.
Childbirth by cesarean section
Childbirth by cesarean section is a surgical procedure carried out to extract the fetus through an opening made in the wall of the abdomen and of the uterus. The procedure takes place in an operating room, under general or epidural anesthesia, and lasts approximately one hour. Childbirth by cesarean section is done if natural childbirth represents a danger for the mother or the child, specifically in the case of insufficient dilation of the cervix, too narrow a pelvis, a poorly positioned placenta, breech position, a particularly large or fragile fetus, or fetal distress. This type of childbirth presents few complications and leaves an unobtrusive scar, approximately 4 inches in length, above the pubis. However, the period that follows (postpartum) is more difficult than after natural birth: later nursing, fatigue, abdominal pain and longer healing time. Throughout the world, approximately 1 of every 7 births is by C-section, with the highest rate in Latin America and the Caribbean, and the lowest in Africa.