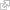The chile pepper
The origins of chile pepper and its culture
The chile pepper, also called the hot pepper, is the fruit of a plant originally from South and Central America. It is a member of the large nightshade family, which includes the eggplant, potato, tamarillo and tomato. One of the first plants to be cultivated in South America (over 7,000 years ago), the chile pepper has been used throughout history for its therapeutic qualities, as a condiment and as a vegetable. It was unknown in Europe before Columbus’s voyages tot he New World in the late 15th century.
Chile peppers were originally grown for decorative purposes; their usefulness as a culinary ingredient was discovered only later. Highly adaptable plants, they migrated quickly, thanks to the Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan, who introduced them into Africa and Asia. Today, chile peppers are cultivated on all continents, growing as a perennial in tropical regions and as an annual in temperate zones.
Species and varieties
The chile pepper is a fleshy berry containing numerous seeds in its inner cavity. The plant on which it grows can reach a height of almost 5 ft (1,5 m).
There are about 10 different species of hot peppers, varying considerably in size, shape, color and flavor. Of these species, annuum and frutescens peppers are of particular culinary importance. Both have a very sharp, almost fiery, flavor.
Nutritional information about the chile pepper
Chile peppers have a higher vitamin C content than oranges. However, the amount of vitamin C they actually provide is minimal considering that they’re most often used in small quantities and in cooked form.
The hot taste of the chile pepper comes from its capsaicin, an alkaloid that is very powerful and that stimulates salivation and causes the gastric juices to flow, thus aiding digestion. The frutescens varieties of chiles contain up to 20 times more capsaicin than sweet peppers.
The Scoville scale measures human tolerance to the sharpness of chiles, with a range up to 300,000 units. The jalapeño pepper is rated between 1,500 and 3,000 on this scale, the cayenne pepper between 20, 000 and 60,000, and Tabasco® Sauce between 80,000 and 120,000.