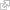The Galaxies
A galaxy is a conglomeration of billions of stars and interstellar matter held together by gravity. Each galaxy forms a bright island lost in the immense black sea of the universe. It is estimated that the universe contains 100 billion galaxies and that each of them contains an average of 100 billion stars. Dwarf galaxies contain only a few million, while giant galaxies contain trillions. The diameter of galaxies ranges from about 3,000 to more than 500,000 light-years. Galaxies apparently formed from diffuse clouds of gas and primordial matter about two billion years after the Big Bang.
Classification of the galaxies
In 1925, the astronomer Edwin Hubble designed a simple method for classifying galaxies. We are still using this method today. He first identified three main shapes: elliptical, spiral and irregular galaxies. Later, he added a fourth one, the lenticular shape.
Characterizing about 60 percent of observed galaxies, the spiral is the most common shape. Spiral galaxies have curved, spiral-shaped arms on the sides of their nucleus. They are classified Sa, Sb or Sc according to the size of their nucleus and how tightly the spiral arms are wound. The Milky Way, the galaxy where our solar system is located, is an Sb-type spiral galaxy. An estimated 20 percent of known galaxies have a lenticular form, 15 percent are elliptical and only about 5 percent are irregular.
Classification of the galaxies
In 1925, the astronomer Edwin Hubble designed a simple method for classifying galaxies. We are still using this method today. He first identified three main shapes: elliptical, spiral and irregular galaxies. Later, he added a fourth one, the lenticular shape.
Characterizing about 60 percent of observed galaxies, the spiral is the most common shape. Spiral galaxies have curved, spiral-shaped arms on the sides of their nucleus. They are classified Sa, Sb or Sc according to the size of their nucleus and how tightly the spiral arms are wound. The Milky Way, the galaxy where our solar system is located, is an Sb-type spiral galaxy. An estimated 20 percent of known galaxies have a lenticular form, 15 percent are elliptical and only about 5 percent are irregular.
Our Galaxy: the Milky Way
Seen from Earth, the Milky Way forms a narrow, dim cloud crossing the nocturnal sky from one side to the other. It looks a little like a stream of milk, which is what inspired the ancient Greeks to name it the Milky Way. It is difficult to determine the exact shape of our galaxy. The fact that we are within it means that we cannot see it in its entirety.
Composed of over 100 billion stars forming a large disk with spiral arms, our galaxy is about 10 billion years old. As for our solar system, it would be only 5 billion years old. It is located on the periphery of the Galaxy, in the Orion Arm. In the center of the Milky Way is a black hole, which results when the core of a massive star collapses. The gravitational force is then so strong that not even light can escape.