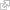Earth: a rocky planet
Earth’s crust is entirely made up of different kinds of rocks. Although they may appear solid and indestructible, rocks change continuously over time, forming, deforming, and transforming into other kinds of rock. They may be pushed deep inside the planet only to resurface later on. In this way, rocks are recycled by nature, in a complex process that may last millions of years. Some rocks, like the very first ones that appeared on Earth, were formed from magma, a fiery liquid rock buried in the planet’s mantle. Some formed out of other kinds of rocks that already existed.
The origins of rocks
Many rocks form deep inside Earth. Some are made of magma that has cooled down and solidified. These are called igneous rocks. On the surface, rocks slowly crumble as they are battered by wind, ice, and water. The rock fragments are washed into rivers, lakes, or oceans, where they sink to the bottom and combine with the remains of animals and plants. Over time, the fragments and remains bond together and harden to form sedimentary rocks. Igneous and sedimentary rocks sometimes sink slowly into the ground, where they are crushed, heated, and deformed by the weight and movement of Earth’s crust. They are transformed into a third type of rock, called metamorphic rock.
Examples of rocks
Rocks are combinations of one or more minerals, which are nonliving solid substances produced by nature. The huge variety of rocks can be divided into three general categories: sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic.

Granite
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock that forms at the bottom of oceans. It is mainly composed of the shells of very tiny marine animals. This is why limestone often contains fossils.
Marble
Basalt
Slate
Rock salt
- "Geology" section
Granite is an igneous rock that is extremely hard and durable. Pink granite is often used in the construction of monuments and buildings.
Heat or pressure can transform limestone into marble, a metamorphic rock of great value that is streaked with swirling patterns of different colors.

Basalt is an igneous rock that forms when magma rises to Earth’s surface. There it erupts from volcanoes in the form of lava and hardens very quickly on contact with the air or water.
Slate is a metamorphic rock that is easy to separate into flakes or sheets. It may be black, gray, or green. Among other things, slate is used on roofs and blackboards.
Rock salt is a crumbly, sedimentary rock that forms when seawater evaporates and leaves a deposit of salt behind. The table salt we use in cooking sometimes comes from this kind of rock.
Also see:
In the Visual Dictionary:
In the encyclopedic capsules :